Analysis U2OS cells
Analysis of ALK2 interactions in U2O Scells
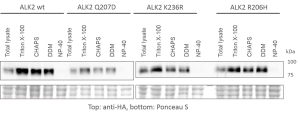
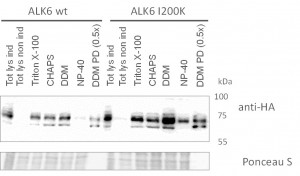
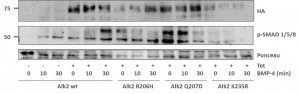
- To characterize interactions involving ALK2 in U2OS cells, transient transfection was used to express wild type or R206H variants of ALK2
- Transiently expressing U2OS were either used unstimulated, or were stimulated with BMP4
- Datasets from unstimulated and BMP4 stimulated cells were compared to identify changes in the protein interaction network after activation of the BMP pathway
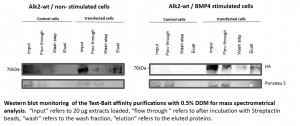
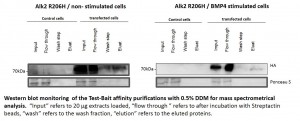
Pilot purification experiments using U2OS cells
- Cells were transiently transfected with ALK2 wild type expression constructs
- Transiently expressing cells were either used as non-stimulated control or stimulated with BMP4
- Small scale pilot purifications were carried out according to the optimized protocol developed with Hek293 cells
- Cells were transiently transfected with ALK2 R206H expression constructs
- Transiently expressing cells were either used as non-stimulated control or stimulated with BMP4
- Small scale pilot purifications were carried out according to the optimized protocol developed with Hek293 cells
Large scale purification of ALK2 from unstimulated U2OS cells
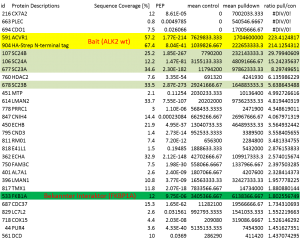
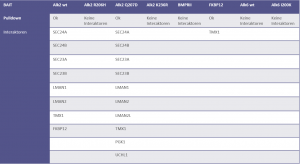
- Volcano-Plot of final merged datasets for ALK2 R206H and control
- Significantly enriched complex partners for ALK2 R206H are boxed
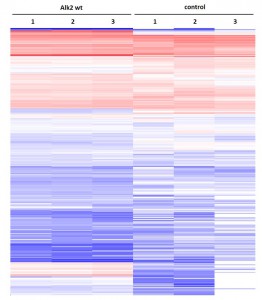
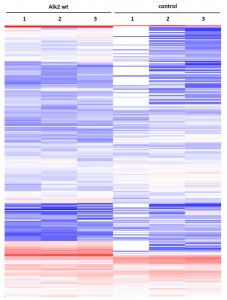
- Primary dataset of large scale purifications for ALK2 wild type
- Triplicate purifications are shown for ALK2 wild type and control
- Color coding shows variations in relative abundance of complex partners identified
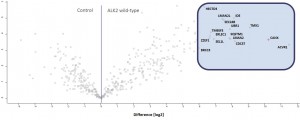
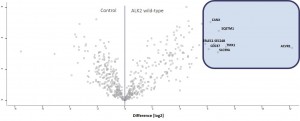
- Volcano-Plot of final merged datasets for ALK2 wild type and control
- Significantly enriched complex partners for ALK2 wild type are boxed
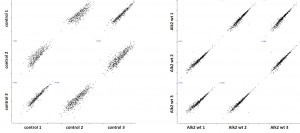
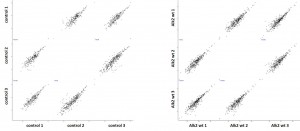
- Scatter plots of triplicate purifications are shown
- Control purifications and ALK2 R206H purifications are shown to demonstrate reproducibility
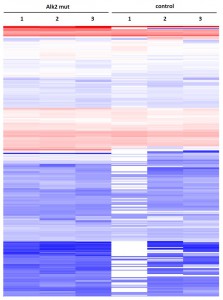
- Primary dataset of large scale purifications for ALK2 R206H
- Triplicate purifications are shown for ALK2 R206H and control
- Color coding shows variations in relative abundance of complex partners identified

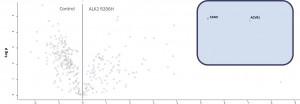
- Volcano-Plot of final merged datasets for ALK2 R206H and control
- Significantly enriched complex partners for ALK2 R206H are boxed
- Scatter plots of triplicate purifications from BMP4 stimulated cells are shown
- Control purifications and ALK2 wild type purifications are shown to demonstrate reproducibility
- Primary dataset of large scale purifications for ALK2 wild type from BMP4 stimulated cells
- Triplicate purifications are shown for ALK2 wild type and control
- Color coding shows variations in relative abundance of complex partners identified
- Volcano-Plot of final merged datasets for ALK2 wild type and control BMP4 stimulated cells
- Significantly enriched complex partners for ALK2 wild type are boxed
- Scatter plots of triplicate purifications from BMP4 stimulated cells are shown
- Control purifications and ALK2 R206H purifications are shown to demonstrate reproducibility
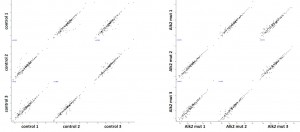
- Primary dataset of large scale purifications for ALK2 R206H from BMP4 stimulated cells
- Triplicate purifications are shown for ALK2 R206H and control
- Color coding shows variations in relative abundance of complex partners identified
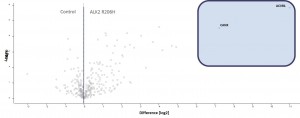
- Volcano-Plot of final merged datasets for ALK2 R206H and control BMP4 stimulated cells
- Significantly enriched complex partners for ALK2 R206H are boxed
 Results: Purification of ALK2 complexes from U2OS cells
Results: Purification of ALK2 complexes from U2OS cells
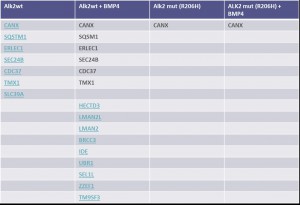
- For ALK2 wild type purified from unstimulated U2OS cells, 8 interactors were identified
- Interactors were mainly involved in receptor sorting, recycling and degradation
- Stimulation of U2OS cells with BMP4 led to the identification of 15 interactors
- 9 additional interactors were identified upon BMP4 stimulation, one interaction was lost
- The ALK2 R206H mutant showed a strongly reduced interaction network: only one interactor was identified
- Stimulation with BMP4 did not change the interaction network of ALK2 R206H
Comparison of ALK2 wild type and R206H interactors identified
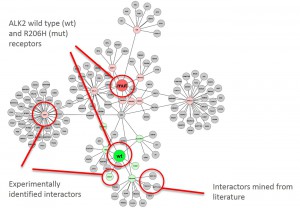
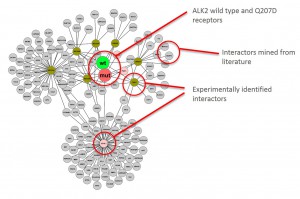
Graphical representation of ALK2 interaction networks
- Merged interaction network of all ALK2 complexes identified (wild type vs R206H; unstimulated vs stimulated)
- Graphical representation was done using Cytoscape
Summary: ALK2interaction network in U2OScells
- The interaction network of ALK2 in U2OS cells shows a large number of proteins involved in receptor sorting and turnover
- Interactors include chaperones, components of the ubiquitination pathway and components of the ERAD pathway
- Stimulation with BMP4 leads to additional interaction of ALK2 with several lysosomal proteins and E3 ubiquitin ligases
- In contrast, the mutant ALK2 R206H does not show interactions with components of either the ubiquitination or ERAD pathways
- The only identified interaction involving ALK2 R206H is with the calcium binding protein calnexin (CANX)